–by Ginger Keys
Dynamic Data Masking is a SQL Server 2016 feature that can be deployed as part of your overall security strategy. Data masking is not intended as a primary security solution, but provides a way to obfuscate or hide characters in data such as social security numbers, credit card numbers, email addresses, and other possibly sensitive data so that end users (or non-privileged users) are not able to see this sensitive data. Data masking hides data by placing X’s or 0’s in place of characters in a data field. For example a masking rule can be defined that masks all but the last four digits of any social security number or credit card number in the result set of any query. A social security number could look like xxx-xx-2345, or an email could display as Gxxxxxx@xxxxx.com.
Let’s be clear…Data masking is not encryption! With data masking, data on the back end is still visible. True encryption like transparent data encryption (TDE) and column level encryption is meant to protect the data in case the physical media (like drives or backup tapes) are stolen, allowing bad guys to restore or attach the database and steal data. Whereas TDE and column level encryption actually change and scramble the backend data, data masking only hides the data in the query results for end users.
Data is not masked on the physical media or storage device, rather it simply obscures the output or the display of the data, based on whether the user is normal or privileged. Data masking hides the sensitive data in the result set or output of a query over designated database fields, however the data in the database is not changed. Because data masking rules are applied only to the query results, many applications can mask sensitive data without having to modify existing queries. In addition to using this feature in conjunction with best practices such as encryption, security is further enhanced by not allowing users to execute ad hoc queries, as the data can be easily unmasked by using a CAST statement.
Pros
Benefits of the data masking feature:
Cons
Disadvantages of data masking:
There are four ways to mask the data: DEFAULT(), EMAIL(), PARTIAL(), and RANDOM(). Each of these produces different masked values for different data types. PARTIAL() allows you to customize the masking somewhat with a prefix and suffix of the actual data and padded string for character data. For full explanation of defining your data mask, go here https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/mt130841.aspx
In order to make the dynamic data masking feature work when connecting through an end user application, use security enabled connection string rather than the original one. The following is a link for connecting to a database through the security enabled connection string: https://www.connectionstrings.com/sql-server/
Data Masking Example
You can mask data in your table columns by either creating your table with masked columns, or altering an already existing table for masking. Below is an example of masking data in an existing table.
— alter existing table column
USE AdventureWorks2014
GO
ALTER TABLE HumanResources.Employee
ALTER COLUMN NationalIDNumber
ADD MASKED WITH (FUNCTION = ‘PARTIAL(0, “xxx-xx-“, 4)’)
–create a Read Only user
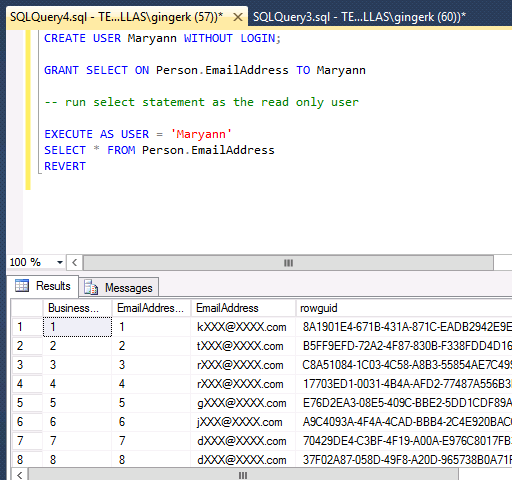
CREATE USER Maryann WITHOUT LOGIN;
GRANT SELECT ON HumanResources.Employee TO Maryann;
You can see below when the select statement is run as a privileged user, all characters are visible in the query results.
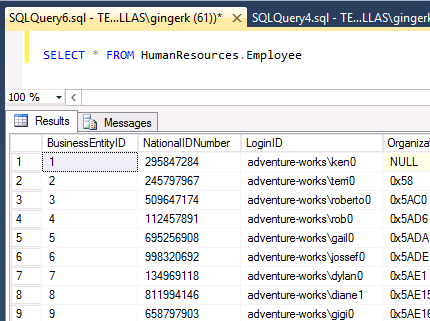
SELECT * FROM HumanResources.Employee — this will show clear data – run as privileged user
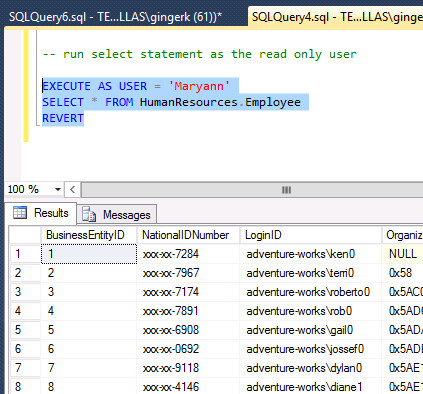
But when the select statement is run as the read-only user as shown below, the sensitive data is masked in the query results.
–run select statement as the read only user
EXECUTE AS USER = ‘Maryann’
SELECT * FROM HumanResources.Employee
REVERT
Below is an example of a masked email address, selected as a read-only user:
Conclusion
The purpose of dynamic data masking is to limit exposure of sensitive data, preventing users who should not have access to the data from viewing it. With today’s FERPA and HIPAA laws, along with a growing concern over identity theft and security, data masking provides an extra layer of privacy and security. Dynamic data masking is complementary to other SQL Server security features (auditing, encryption, row level security…) and it is highly recommended to use this feature in conjunction with them.
For more information about blog posts, concepts and definitions, further explanations, or questions you may have…please contact us at SQLRx@sqlrx.com. We will be happy to help! Leave a comment and feel free to track back to us. Visit us at www.sqlrx.com!